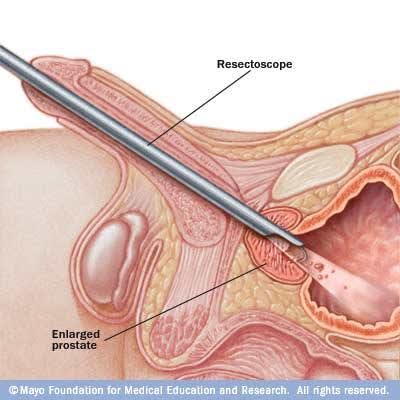
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is the surgical removal of part of the prostate gland. It is one option available to relieve the symptoms of an enlarged prostate or other benign (non-cancerous) prostate disease. It is by far the most common of the surgical procedures used for benign prostate disease.
Prostate problems that occur:
The three main problems that occur in the prostate include:
- inflammation (prostatitis)
- Non-cancerous enlargement of the middle part of the prostate. This is also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- Cancer of the prostate. This occurs mostly at the back of the prostate, but sometimes also occurs in the area where the prostate is enlarged due to BPH.
Prostate size and blocking of the urethra:
- Problems with starting urination
- Reduced flow
- Frequent urination, particularly at night
- Urgency and possible urgency incontinence
- Passing drops of urine involuntarily after you think you’ve finished
- Blood in the urine – although this can never be assumed to be due to the prostate until other causes have been excluded
The procedure:
TURP is sometimes referred to as a ‘re-bore’. It involves inserting a slender instrument through the urethra into the bladder. Only the middle part of the prostate is removed to allow you to pass urine more easily.TURP is used most often for non-cancerous blockage, but may also be used in some cases of prostate cancer. This is the most common form of surgery (around 95 per cent of surgical procedures). The average hospital stay is three to four days.
What to expect post surgery:
- A catheter to be insitu
- Irrigation flowing through that catheter, clearing the bladder of any blood from the surgery
- The sensation you want to urinate – Due to catheter
- The irrigation will cease when the doctor is happy with the colour of your urine (Not too dark blood stained) and the catheter will come out when doctor requests
- You will then have a TOV (Trial of void) trial of void means that they will get you to urinate in a bottle and then call the nurse when finished and she will do a bladder scan on your bladder to see if there is any residual volume remaining in the bladder
- On two occasions the urine remaining in your bladder must be less than 150mls but this number can vary depending on the size of your bladder which will be discussed with the nurse and doctor.
